Frequency and Wavelength (λ) 3c1, 3c2, 3c3
Alternating Current known as AC reverses its direction several/many times per second.
Wavelength (λ)
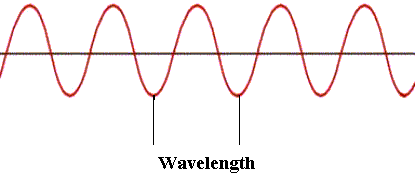
The distance between one peak and the next is called the wavelength and is measured in metres or centimetres. The symbol λ is often used for wavelength.
This shape of graph is known as a sine wave. An oscillator is used to produce sine waves.
Frequency
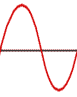 This is 1 cycle.
When this happens once in a second it is called 1 Hertz (1Hz). Frequency
is measured in Hertz (Hz).
This is 1 cycle.
When this happens once in a second it is called 1 Hertz (1Hz). Frequency
is measured in Hertz (Hz).
When this happens 50 times a second this is 50 Hertz (50 Hz). The mains electricity supply in the UK alternates 50 times a second or 50 Hz.
Audio Frequency (AF)
People with normal hearing can hear frequencies from 100 Hz to 15kHz (15,000 Hz). This range of frequencies are called Audio Frequencies (AF)
Audio communication (electrical signals in wires etc) 300Hz to 3kHz (3,000 Hz)
Click here to listen to a 250 Hz audio tone (Requires Windows Media Player)
Click here to listen to a 2.5 kHz (2500 Hz) audio tone (Requires Windows Media Player)
Radio Frequency (RF)
Most Radio signals change direction (alternate or oscillate) between 1 Million and 1 Thousand Million times per second (between 1 MHz and 1000 MHz).
Medium Frequency (MF) radio frequencies are in the range 300 kHz to 3 MHz
High Frequency (HF) radio frequencies are in the range 3 MHz to 30 MHz
Very High Frequency (VHF) radio frequencies are in the range 30 MHz to 300 MHz
Ultra High Frequency (UHF) radio frequencies are in the range 300 MHz to 1000 MHz
Radio frequency sine waves are produced by oscillators.
Radio Frequency Bands
Ranges of similar Radio Frequencies are called Bands. Frequency Bands are allocated for particular uses (e.g. Broadcasting, Aeronautical, Maritime, Amateur). The table below shows how some of the VHF radio frequencies are divided up into bands.
Radio Frequency Band |
Use |
|
87.5 – 108.0 MHz |
Broadcasting |
|
108.0 – 117.975 MHz |
Aeronautical Radio Navigation |
|
117.95 – 137.0 MHz |
Aeronautical Mobile |
|
137.0 – 138.0 MHz |
Space Operations & Space Research |
|
138.0 – 144.0 MHz |
Land Mobile |
|
144.0 – 146.0 MHz |
Amateur & Amateur Satellite |
|
146.0 – 149.9 MHz |
Mobile (except aeronautical mobile) |
|
149.9 – 150.05 MHz |
Radionavigation – Satellite |
|
150.05 – 152.0 MHz |
Radio Astronomy |
|
152.0 – 156.0 MHz |
Land Mobile |
|
156.0 – 158.525 MHz |
Maritime Mobile |
|
158.525 – 160.6 MHz |
Land Mobile |
|
160.6 – 160.975 MHz |
Maritime Mobile |
As you can see amateurs share the use of the radio spectrum with many other users. You do not need to learn this table.
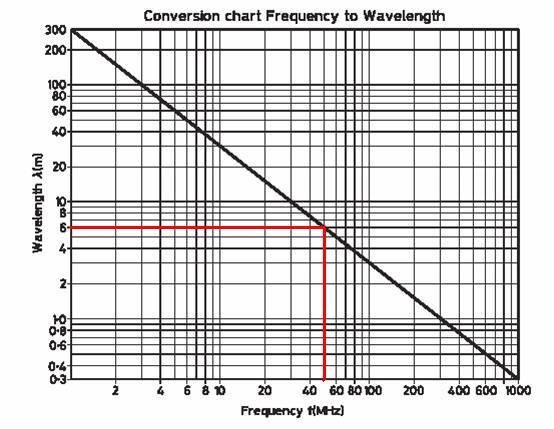
Frequency & Wavelength
As you can see from the graph below there is a relationship between Frequency and Wavelength. As the Wavelength reduces, the frequency increases. You can use the graph to convert a wavelength of 6m to a frequency of 50MHz for example.